Determining the views, current situations, and needs of preschool teachers about STEAM education: Case of Turkey
Abstract
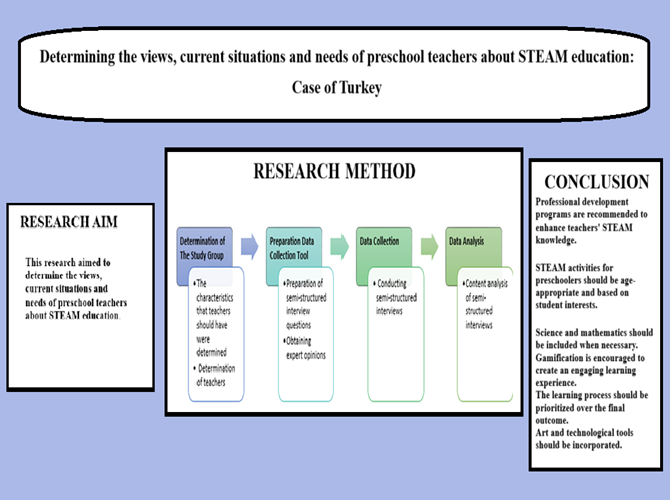
This research aimed to determine preschool teachers' views, the current situation, and schools regarding STEM education. A case study, which is a qualitative research approach, was used for this research. The study group was determined by the purposeful sampling method. The research study group comprises 10 preschool teachers with STEM education courses. In the research, semi-structured interviews were conducted to determine preschool teachers' opinions. Semi-structured interviews lasted between 9 and 15 minutes. The interview was analyzed with content analysis. As a result of the research, it was determined that preschool teachers have limited knowledge about STEAM, have positive effects on children, have educational and activity needs, and have difficulty finding resources. According to teachers, STEAM activities for preschool students should be age/level appropriate, selected according to the student's interest, should include science and mathematics subjects, if necessary, the process should be gamified, children should have fun in the process, children should be taken to the center starting from the problem situation, supported by art and art and technological tools.
Keywords
Full Text:
Download PDFReferences
Aldemir, J., & Kermani, H. (2017). Integrated STEM curriculum: Improving educational outcomes for Head Start children. Early Child Development and Care, 187(11), 1694-1706. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2016.1185102.
Angier, N. (2010). STEM education has little to do with flowers. The New York Times, D2.
Bagiati, A., Yoon, S. Y., Evangelou, D., & Ngambeki, I. (2010). Engineering curricula in early education: Describing the landscape of open resources. Early Childhood Research & Practice, 12(2), n2. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ910909.pdf.
Birinci, G., Kılıçer, K., Ünlüer, S., & Kabakçı, I. (2009). Eğitim teknolojisi alanında yapılan durum çalışması araştırmalarının yöntemsel değerlendirilmesi [Methodological evaluation of case study research in the field of educational technology]. Uluslararası Bilgisayar ve Öğretim Teknolojileri Sempozyumu. Karadeniz Teknik Üniversitesi, Trabzon.
Bower, M., & Sturman, D. (2015). What are the educational affordances of wearable technologies? Computers & Education, 88, 343-353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compedu.2015.07.013.
Boy, G. A. (2013, August). From STEM to STEAM: toward a human-centred education, creativity & learning thinking. In Proceedings of the 31st European conference on cognitive ergonomics (pp. 1-7).
Breiner, J. M., Harkness, S. S., Johnson, C. C., & Koehler, C. M. (2012). What is STEM? A discussion about conceptions of STEM in education and partnerships. School Science and Mathematics, 112(1), 3–11. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1949-8594.2011.00109.x
Bryan, L. A., Moore, T. J., Johnson, C. C., & Roehrig, G. H. (2015). Integrated STEM education. In C. C. Johnson, T. J. Moore, & E. E. Peters-Burton (Eds.), STEM roadmap: A framework for integrated STEM education (pp. 23–37). New York, NY: Routledge.
Butera, G., Horn, E. M., Palmer, S. B., Friesen, A., & Lieber, J. (2016). Understanding Science, Technology, Engineering, Arts, and Mathematics (STEAM) within Early Childhood Special Education. Handbook of Early Childhood Special Education, 143-161. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-28492-7_9
Bybee, R. W. (2013). The case for STEM education: Challenges and opportunities. NSTA Press.
Chesloff, J. D. (2013). STEM education must start in early childhood. Education Week, 32(23), 27-32. https://d1wqtxts1xzle7.cloudfront.net/72533316/1303.
Connor, A. M., Karmokar, S., & Whittington, C. (2015). From STEM to STEAM: Strategies for enhancing engineering and technology education. International Journal for Engineering Pedagogy, 5(2), 37–47. https://doi.org/10.3991/ijep.v5i2.4458
Creswell, J. W., Hanson, W. E., Clark Plano, V. L., & Morales, A. (2007). Qualitative research designs: Selection and implementation. The counseling psychologist, 35(2), 236-264.
Creswell, J. W. (2012). Educational research: planning, conducting, and evaluating quantitative research (4th editionı). Boston: Pearson Education Inc.
Dare, E. A., Ring-Whalen, E. A., & Roehrig, G. H. (2019). Creating a continuum of STEM models: exploring how K-12 science teachers conceptualize STEM education. International Journal of Science Education, 41(12), 1701–1720. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2019.1638531
Daugherty, M. K. (2013). The Prospect of an “A” in STEM Education. Journal of STEM Education: Innovations and Research, 14(2), 10–15. https://www.jstem.org/jstem/index.php/JSTEM/article/view/1744.
DeJarnette, N. (2012). America's children: Providing early exposure to STEM (science, technology, engineering and math) initiatives. Education, 133(1), 77-84.
Dilek, H., Tasdemir, A., Konca, A. S., & Baltaci, S. (2020). Preschool students' science motivation and process skills during inquiry-based STEM activities. Journal of Education in Science Environment and Health, 6(2), 92-104. https://doi.org/10.21891/jeseh.673901.
Dockett, S., & Perry, B. (2004). Starting school: Perspectives of Australian children, parents and educators. Journal of Early Childhood Research, 2(2), 171-189.
Dubek, M., DeLuca, C., & Rickey, N. (2021). Unlocking the potential of STEAM education: How exemplary teachers navigate assessment challenges. The Journal of Educational Research, 114(6), 513-525. https://doi.org/10.1080/00220671.2021.1990002
Fraenkel, J. R., Wallen, N. E., & Hyun, H. H. (2011). How to design and evaluate research in education (8th ed.). NY: McGraw-Hill.
Güldemir, S. (2019). The effect of STEM activities on creativity in preschool [Unpublished Master's Thesis]. Recep Tayyip Erdoğan University.
Herro, D., & Quigley, C. (2017). Exploring teachers’ perceptions of STEAM teaching through professional development: implications for teacher educators. Professional Development in Education, 43(3), 416-438. https://doi.org/10.1080/19415257.2016.1205507
Herschbach, D. R. (2011). The STEM initiative: Constraints and challenges. Journal of STEM Teacher Education, 48(1), 96–112 https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ952045
Honey, M., Pearson, G., & Schweingruber, A. (2014). STEM integration in K12 education: status, prospects, and an agenda for research. Washington: National Academies Press.
Hong Wang, H., Lin, H. S., Chen, Y. C., Pan, Y. T., & Hong, Z. R. (2021). Modelling relationships among students’ inquiry-related learning activities, enjoyment of learning, and their intended choice of a future STEM career. International Journal of Science Education, 43(1), 157-178. https://doi.org/10.1080/09500693.2020.1860266
Jamil, F. M., Linder, S. M., & Stegelin, D. A. (2018). Early childhood teacher beliefs about STEAM education after a professional development conference. Early Childhood Education Journal, 46, 409-417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-017-0875-5.
John, M. S., Sibuma, B., Wunnava, S., Anggoro, F., & Dubosarsky, M. (2018). An iterative participatory approach to developing an early childhood problem-based STEM curriculum. European Journal of STEM Education, 3(3), 07. https://doi.org/10.20897/ejsteme/3867.
Katz, L. G. (2010). STEM in the early years. Early childhood research and practice, 12(2), 11-19.
Keçeci, G. (2023). Determining Pre-Service Science Teachers' Understanding About STEM Education. Journal of Baltic Science Education, 22(5), 833. https://doi.org/10.33225/jbse/23.22.833
Kennedy, T. J., & Odell, M. R. (2014). Engaging students in STEM education. Science Education Inter, 25(3), 246-258. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1044508.pdf.
Kermani, H., & Aldemir, J. (2015). Preparing children for success: Integrating science, math, and technology in early childhood classroom. Early Child Development and Care, 185(9), 1504–1527. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2015.1007371
Kewalramani, S., Palaiologou, I., & Dardanou, M. (2020). Children’s engineering design thinking processes: The magic of the ROBOTS and the power of BLOCKS (electronics). EURASIA Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 16(3). https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/113247
Labov, J. B., Reid, A. H., & Yamamoto, K. R. (2010). Integrated biology and undergraduate science education: A new biology education for the twenty-first century? CBE Life Science Education, 9, 10–16. https://doi.org/10.1187/cbe.09-12-0092
Lee, J. S. (2006). Preschool teachers' shared beliefs about appropriate pedagogy for 4-year-olds. Early Childhood Education Journal, 33, 433-441.
Lin, X., Yang, W., Wu, L., Zhu, L., Wu, D., & Li, H. (2021). Using an inquiry-based science and engineering program to promote science knowledge, problemsolving skills and approaches to learning in preschool students. Early Education and Development, 32(5), 695-713. https://doi.org/10. 1080/10409289.2020.1795333.
Lowrie, T., & Larkin, K. (2020). Experience, represent, apply (ERA): A heuristic for digital engagement in the early years. British Journal of Educational Technology, 51(1), 131-147. https://doi.org/10.1111 /bjet.12789
McClure, E. R., Guernsey, L., Clements, D. H., Bales, S. N., Nichols, J., KendallTaylor, N., & Levine, M. H. (2017). STEM starts early: Grounding science, technology, engineering, and math education in early childhood. New York: The Joan Ganz Cooney Center at Sesame Workshop.
Mercan, Z., & Kandır, A. (2019). Preschool teachers' opinions regarding STEAM approach in education. Journal of Current Researches on Educational Studies, 8(2), 15-28. doi: 10.26579/jocures-9.1.2
Merriam, S. B. (1998). Qualitative research and case study applications in education. California: Jossey-Bass.
Miles, M. B., & Huberman, A. M. (1994). Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook. Sage.
Moomaw, S., & Davis, J. A. (2010). STEM comes to preschool. YC: Young Children, 65(5).
Moore, T. J., Johnston, A. C., & Glancy, A. W. (2020). A synthesis of conceptual frameworks and definitions. In C. C. Johnson, M. J. MohrSchroeder, T. J. Moore, & E. L. D (Eds.), Handbook of research on STEM education, (pp. 3–16). Routledge.
Neuman, D. (2014). Qualitative research in educational communications and technology: A brief introduction to principles and procedures. Journal of Computing in Higher Education, 26, 69-86.
Neuman, W. L. (2012). Social Research Methods: Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches Volume III (5th Edition). Istanbul: Publication Room.
Ng, A., Kewalramani, S., & Kidman, G. (2022). Integrating and navigating STEAM (inSTEAM) in early childhood education: An integrative review and in STEAM conceptual framework. Eurasia Journal of Mathematics, Science and Technology Education, 18(7), 2133. https://doi.org/10.29333/ejmste/12174.
Parette, H., Quesenberry, A., & Blum, C. (2010). Missing the boat with technology usage in early childhood settings: A 21st Century view of developmentally appropriate practice. Early Childhood Education Journal, 37, 335-343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10643-009-0352-x
Park, M. H., Dimitrov, D. M., Patterson, L. G., & Park, D. Y. (2017). Early childhood teachers’ beliefs about readiness for teaching science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. Journal of Early Childhood Research, 15(3), 275–291. https://doi.org/10.1177/1476718X15614040.
Peppler, K. (2013). New Opportunities for Interest-Driven Arts Learning in a Digital Age. Wallace Foundation.
Riechert, S. E., & Post, B. K. (2010). From skeletons to bridges & other STEM enrichment exercises for high school biology. The American Biology Teacher, 72(1), 20-22. https://doi.org/10.1525/abt.2010.72.1.6.
Rinke, C. R., Gladstone-Brown, W., Kinlaw, C. R., & Cappiello, J. (2016). Characterizing STEM teacher education: Affordances and constraints of explicit STEM preparation for elementary teachers. School Science and Mathematics, 116(6), 300–309. https://doi.org/10.1111/ssm.12185
Sanders, M. (2009). STEM, STEM education, STEMmania. The Technology Teacher, 68(4), 20–26. http://hdl.handle.net/10919/51616
Schroeder, E. L., & Kirkorian, H. L. (2016). When seeing is better than doing: Preschoolers’ transfer of STEM skills using touchscreen games. Frontiers in Psychology, 7, 1377. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2016.01377
Scientific and Technological Research Council of Türkiye [TÜBİTAK] (2004). National science and technology policies, 2003-2023 strategy document. http://www.tubitak.gov.tr/tubitak_content_files.
Shrestha, P. (2021). Integrating STEAM Education in Preschool and Kindergarten Classrooms: A Case Study (Doctoral dissertation, California State University, Sacramento).
Simoncini, K., & Lasen, M. (2018). Ideas about STEM among Australian early childhood professionals: How important is STEM in early childhood education? International Journal of Early Childhood, 50(3), 353–369. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13158-018-0229-5
Sousa, D. A., & Pilecki, T. J. (2013). From STEM to STEAM: Using Brain Compatible Strategies to Integrate the Arts. Corwin Press.
Süldür, S. (2019). Determining the opinions of classroom teachers towards STEM education (Master's thesis).
Tank, K. M., Rynearson, A. M., & Moore, T. J. (2018). Examining Student and Teacher Talk within Engineering Design in Kindergarten. European Journal of STEM Education, 3(3), 10. https://eric.ed.gov/?id=EJ1190717.
Tashakkori, A., & Teddlie, C. (2003). Issues and dilemmas in teaching research methods courses in social and behavioural sciences: US perspective. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 6(1), 61-77. https://doi.org/10.1080/13645570305055
Tippett, C. D., & Milford, T. M. (2017). Findings from a kindergarten classroom: Making the case for STEM in early childhood education. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 15(1), 67-86. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-017-9812-8.
Turiman, P., Omar, J., Daud, A. M., & Osman, K. (2012). Fostering the 21st century skills through scientific literacy and science process skills. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 59, 110-116. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.2466
Weng, J., & Li, H. (2020). Early technology education in China: A case study of Shanghai. Early Child Development and Care, 190(10), 1574-1585. https://doi.org/10.1080/03004430.2018.1542383
Yakman, G. (2008). STEAM education: An overview of creating a model of integrative education. In Pupils’ attitudes towards technology (PATT-19) conference: Research on technology, innovation, design & engineering teaching, Salt Lake City, Utah. https://www.iteea.org/File.aspx.
Yamak, H., Bulut, N., & Dündar, S. (2014). 5. sınıf öğrencilerinin bilimsel süreç becerileri ile fene karşı tutumlarına FeTeMM etkinliklerinin etkisi [The effects of STEM activities on 5th grade students' scientific process skills and attitudes towards science]. Gazi Üniversitesi Gazi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi, 34(2), 249-265. https://doi.org/10.17152/gefd.15192.
Yıldırım, A., & Şimşek, H. (2013). Qualitative Research Methods in Social Sciences (6th Edition). Ankara: Seçkin Publishing.
Yildiz, S., & Zengin, R. (2021). Effect of science education provided with digital and ın-class games on the scientific process skills of preschool students. Journal of Science Learning, 4(4), 385-393. https://doi.org/10.17509/jsl.v4i4.30620
Yıldız, S., & Zengin, R. (2023). Türkiye'de okul öncesi fen eğitimine yönelik yapılan araştırmaların analizi: meta-sentez çalışması. [Analysis of research conducted on preschool education in Turkey: a meta-synthesis study]. Fırat Üniversitesi Sosyal Bilimler Dergisi, 33(3), 1183-1197. https://doi.org/10.18069/firatsbed.1232738
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17509/jsl.v8i1.68155
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2025 Selin Yıldız, Raşit Zengin

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi 229 Bandung 40154, West Java, Indonesia











