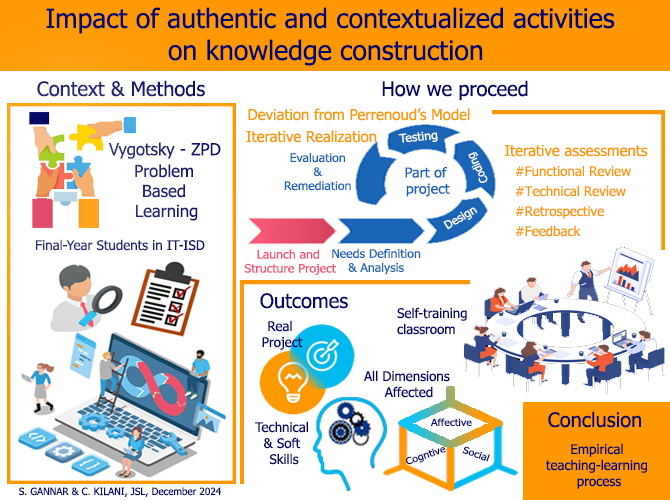
Contextualized Learning and Social Constructivism: Implementing a Project-Based Approach in Information Systems Development Education
Abstract
Keywords
Full Text:
Download PDFReferences
Adam, S. F. (2006). An introduction to learning outcomes: A consideration of the nature, function and position of learning outcomes in the creation of the European Higher Education Area. https://api.semanticscholar.org/CorpusID:8549631
Ajjawi, R., & Boud, D. (2018). Examining the nature and effects of feedback dialogue. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 43(7), 1106–1119. https://doi.org/10.1080/02602938.2018.1434128
Alias, M., Lashari, T. A., Akasah, Z. A., & Kesot, M. J. (2014). Translating theory into practice: Integrating the affective and cognitive learning dimensions for effective instruction in engineering education. European Journal of Engineering Education, 39(2), 212–232. https://doi.org/10.1080/03043797.2013.838543
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (2018). Classroom assessment and pedagogy. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, 25(6), 551–575. https://doi.org/10.1080/0969594X.2018.1441807
Brousseau, G. P. (1976). Epistemological obstacles and problems in mathematics. The Problematic and Teaching of Mathematics. Retrieved from https://hal.science/hal-00516569v2
Cole, M., & Wertsch, J. V. (1996). Beyond the individual-social antinomy in discussions of Piaget and Vygotsky. Human Development, 39(5), 250–256. https://doi.org/10.1159/000278475
Darnon, C., Buchs, C., & Butera, F. (2006). Buts de performance et de maîtrise et interactions sociales entre étudiants: La situation particulière du désaccord avec autrui. Revue Française de Pédagogie, 155, 35–44. https://doi.org/10.4000/rfp.84
do Carmo, F. M. A., de Oliveira Faustino, J. A., de Lima, M. V. M., Felício, M. S. N. B., Neto, H. B., & Cerqueira, G. S. (2020). Didactic contract from the perspective of the theory of didactical situations. International Journal for Innovation Education and Research, 8(7), 123–134. https://doi.org/10.31686/ijier.vol8.iss7.2460
Guillemette, F. (2020). Moving from the transmissive model to a guided learning model. Issues and Society, 7, 42–73. https://doi.org/10.7202/1073360ar
Hameline, D. (2022). Questions to Daniel Hameline. La Pensée d’Ailleurs, 8, 8–74. https://www.ouvroir.fr/lpa/index.php?id=204 https://doi.org/10.57086/lpa.204
Hernáiz-Pérez, M., Álvarez-Hornos, J., Badia, J. D., Giménez, J. B., Robles, Á., Ruano, V., & San-Valero, P. (2021). Contextualized project-based learning for training chemical engineers in graphic expression. Education for Chemical Engineers, 34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ece.2020.11.003
Khasawneh, A. A., Al-Barakat, A. A., & Almahmoud, S. A. (2022). The effect of error analysis-based learning on proportional reasoning ability of seventh-grade students. Frontiers in Education, 7. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2022.899288
Kumar, A. (2022). Observation method: Observation method view project observation method observation methods. Retrieved from https://www.researchgate.net/publication/360808469_OBSERVATION_METHOD
Larochelle, M., Bednarz, N., & Garrison, J. (Eds.). (1999). Constructivism and education. Educational Studies in Mathematics, 40(1), 93–99. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1003750912432
Leclerc, M. (2007). Project-based learning. Sainte-Foy: Presses de l’Université du Québec. Revue des Sciences de l’Éducation, 33, 261–262.
Leiber, T. (2022). Justifying, contextualizing, and operationalizing performance indicators of learning and teaching: The role of theories and practice of learning and teaching. Quality in Higher Education, 28(2), 120–140. https://doi.org/10.1080/13538322.2021.1951454
Lim, S. W., Jawawi, R., Jaidin, J. H., & Roslan, R. (2023). Learning history through project-based learning. Journal of Education and Learning (EduLearn), 17(1), 67–75. https://doi.org/10.11591/edulearn.v17i1.20398
Marnewick, C. (2023). Student experiences of project-based learning in agile project management education. Project Leadership and Society, 4, 100096. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plas.2023.100096
Maros, M., Korenkova, M., Fila, M., Levicky, M., & Schoberova, M. (2023). Project-based learning and its effectiveness: Evidence from Slovakia. Interactive Learning Environments, 31(7), 4147–4155. https://doi.org/10.1080/10494820.2021.1954036
Morgado, S., Leite, L., & Dourado, L. (2022). Teaching for the contextualized learning of science: A checklist-based science curriculum analysis. Journal of Turkish Science Education, 19(4). https://doi.org/10.36681/tused.2022.163
Muhajirah, M. (2020). Basic of learning theory (behaviorism, cognitivism, constructivism, and humanism). International Journal of Asian Education, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.46966/ijae.v1i1.23
Newton, N. (2010). Exploring Qualitative Methods: The use of semi-structured interviews. Exploring Qualitative Methods, 1(1), 1-11.
Ngo, V. T., Marguet, C., Favre, B., & Buty, C. (2013). Project-based pedagogy: A case study in technological higher education. Essay Research in Science Education, 15, 15–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procs.2023.01.465
O’Brien, B. C., & Battista, A. (2020). Situated learning theory in health professions education research: A scoping review. Advances in Health Sciences Education, 25, 483–509. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10459-019-09900-w
Peralta, N.S., Castellaro, M., Tuzinkievicz, M.A., & Curcio, J.M.C., (2023). Argumentation in young university students: review of research carried out from socioconstructivism. Revista Latinoamericana de Ciencias So- ciales, Niñez y Juventud 21, 1–23. https://doi.org/10.11600/rlcsnj.21.2.5783
Perrenoud, P., (2002). Learning at school through projects: why? how? University of Geneva - Faculty of Psychology and Educational Sciences.URL : Perrenoud - Apprendre à l’école à travers des projets : pourquoi ? comment ? (unige.ch)
Proulx, J. (2004). “Enactivism” ou la théorie cognitive de la «Personnifiaction»: Une tentative pour mieux comprendre notre activité langagière. Journal of the Canadian Association for Curriculum Studies.
Rapanta, C. (2023). Piaget, Vygotsky and young people’s argumentation: Sociocognitive aspects and challenges of reasoning “together” and “alone.” Learning, Culture and Social Interaction, 39, 100698. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lcsi.2023.100698
Sidambarompoulle, D. & Senteni, A. (2007). Professionnaliser la formation des étudiants en travail social: De l'apprentissage individualisé aux communautés d'apprenants. Les Sciences de l'éducation - Pour l'Ère nouvelle, 40, 29-47. https://doi.org/10.3917/lsdle.401.0029
Sze-yeng, F., & Hussain, R. M. R. (2010). Self-directed learning in a socioconstructivist learning environment. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 9, 1913–1917. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2010.12.423
Thien, N.V., Marguet, C., Favre, B., & Buty, C. (2013). Pedagogie par projet: une étude de cas dans l'enseignement superieur technologique. Ensaio Pesquisa em Educação em Ciências, 15, 15-30. DOI:10.1590/1983-21172013150102
Wang, D. (2022). What is ZPD and what are the implications of ZPD for teaching. Journal of Humanities and Education Development, 4(3), 242-244.. DOI:10.22161/jhed.4.3.29.
Wang, S. (2022). Critical Thinking Development Through Project-Based Learning. Journal of Language Teaching and Research, 13(5), 1007–1013. https://doi.org/10.17507/jltr.1305.13
Wijnen, M., Loyens, S. M. M., Wijnia, L., Smeets, G., Kroeze, M. J., & van der Molen, H. T. (2018). Is problem-based learning associated with students’ motivation? A quantitative and qualitative study. Learning Environments Research, 21(2). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10984-017-9246-9
Yu, H. (2024). Enhancing creative cognition through project-based learning: An in-depth scholarly exploration. In Heliyon (Vol. 10, Issue 6). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e27706
Zaretsky, V. K. (2021). One More Time on the Zone of Proximal Development. Cultural-Historical Psychology, 17(2). https://doi.org/10.17759/chp.2021170204
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17509/jsl.v8i1.72667
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2025 Sonia Gannar, Chiraz Kilani

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi 229 Bandung 40154, West Java, Indonesia











