Science and Mathematics Teachers’ Intention Towards Adopting CL4STEM Technology-based Instructional Initiative to Enhance Higher Order Teaching with Equity and Inclusion in Nigeria
Abstract
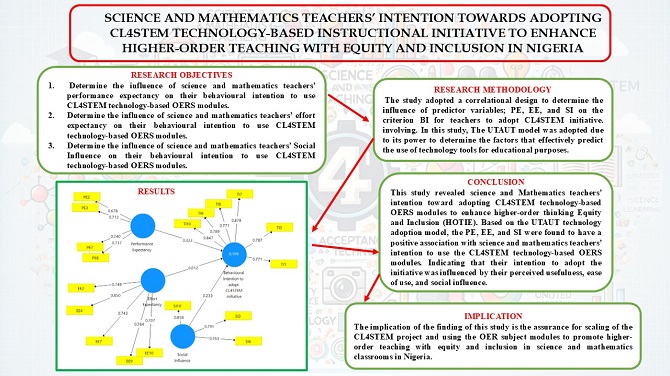
The study examined Nigeria Science and Mathematics Teachers’ intention towards adopting the CL4STEM technology-based instructional (OER) modules to enhance higher-order thinking with Inclusion and Equity (HOTIE). The study adopted a descriptive correlational design. The population of the study was all mathematics and science teachers in some selected Northern States (Niger, Kaduna, and Kano) in Nigeria. The sample size was 100 science and mathematics teachers. The instrument for data collection was structured questionnaires on teachers’ Performance Expectancy, Effort Expectancy, Social Influence, and Behavioural Intention toward adopting the CL4STEM technology-based instructional (OER) modules. Smart PLS version 3, was utilized to test the measurement model, and structural model, and verify the convergent and discriminant validity. The findings show a positive and significant relationship between science and mathematics teachers’ Performance Expectancy, Effort Expectancy, Social Influence, and Behavioural Intention toward adopting the CL4STEM technology-based instructional (OER) modules. It was concluded that teachers’ intention to adopt them in their classroom practices was influenced by their perceived usefulness, ease of use, and social influence. The finding suggests that science and mathematics teachers would most likely sustain the use of CL4STEM technology-based instructional (OER) modules to enhance HOTIE in Nigeria.
Keywords
Full Text:
Download PDFReferences
Abbad M.M. (2021). Using the UTAUT model to understand students’ usage of e-learning systems in developing countries. Education and Information Technologies 26:7205–7224 https://doi.org/10.1007/s10639-021-10573-5
Agarwal, V. (2016). Investigating the convergent validity of organizational trust. Journal of Communication Management, 17(1), 24–39. https://doi.org/10.1108/13632541311300133
Akdeniz, B. E. & C. (2012). Development of a scale to diagnose instructional strategies. Contemporary Educational Technology, 3(2), 141–161.
Al-Gahtani, S. S. (2016). Empirical investigation of e-learning acceptance and assimilation: A structural equation model. Applied Computing and Informatics, 12(1), 27–50. doi:10.1016/j.aci.2014.09.001
Alghazi, S.S.; Kamsin, A.; Almaiah, M.A.; Wong, S.Y.; Shuib, L. (2021) For Sustainable Application of Mobile Learning: An Extended UTAUT Model to Examine the Effect of Technical Factors on the Usage of Mobile Devices as a Learning Tool. Sustainability, 13, 1856. https://doi.org/10.3390/su13041856
Alharbi, S., & Drew, S. (2014). Mobile learning-system usage: Scale development and empirical tests. International Journal of Advanced Research in Artificial Intelligence, 3(11), 31–47. doi:10.14569/ijarai.2014.031105
Al-Sultan, A. T. (2015). Empirical investigation on factors influencing the behavioral intention to use e-library for a private university in Kuwait using the statistical approach in a structure equation model (SEM). Far East Journal of Mathematical Education, 14(1), 25–48. doi:10.17654/fjmefeb2015_025_048
Al Zebidi, A. (2011). The impact of using computer software on students’ Achievement at Al-Qunfudh University College and their attitudes towards it (Unpublished Master's thesis)
Ayele, A. A. & Sreenivasarao, V. (2013). A case study of acceptance and use of electronic library services in universities based on SO-UTAUT model. International Journal of Innovative Research in Computer and Communication Engineering, 1(4), 903–911
Amid, A. & Din, R. (2021). Acceptance and use of massive open online courses: Extending UTAUT2 with personal innovativeness. Journal of Personalized Learning, 4(1): 57-66
Byrne, M., Flood, B., & Willis, P. (2004). Using the student learning framework to explore the variation in academic performance of European business students. Journal of Further and Higher Education, 28(1), 67–78. https://doi.org/10.1080/0309877032000161823
Chan, L. L., & Idris, N. (2017). Validity and reliability of the instrument using exploratory factor analysis and Cronbach’s alpha. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 7(10), 400–410. https://doi.org/10.6007/IJARBSS/v7-i10/3387
Chen, Y. H. (2015). Testing the impact of an information literacy course: Undergraduates’ perceptions and use of the university libraries’ web portal. Library & Information Science Research, 37(3), 263–274. doi:10.1016/j.lisr.2015.04.002
Chen, Y. H., & Chengalur-Smith, I. (2015). Factors influencing students’ use of a library Web portal: Applying course-integrated information literacy instruction as an intervention. The Internet and Higher Education, 26, 42–55. doi:10.1016/j.iheduc.2015.04.005
Chin, K.L. (1999) A study into students’ perceptions of a web-based learning environment. HERDSA Annual International Conference.
Chopra, S., & Rajan, P. (2016). Modeling intermediary satisfaction with mandatory adoption of e-government technologies for food distribution. Information Technologies & International Development, 12(1), 15–34.
Churchill, G. A. (1979). A paradigm for developing better measures of marketing constructs. Journal of Marketing Research, 16(1), 64. https://doi.org/10.2307/3150876
CL4STEM-Nigeria. (2023). Strengthening Secondary School Teacher Capacities for Higher Order Thinking with Inclusion and Equity. Connected Learning for STEM, Ibrahim Badamasi Babangida University, Lapai.
Davis, F. D. (1993). User acceptance of information technology: System characteristics, user perceptions and behavioral impacts. International Journal of Man-Machine Studies, 38(1), 475–487.
Echeng, R., Usoro, A., & Majewski, G. (2013, July). Acceptance of Web 2.0 in Learning in higher education: an empirical study of a Scottish university. In WBC 2013 July conference proceedings on e-learning (pp. 30-38) http://repository.cmu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=1168&context=hsshonors
Federal Ministry of Education (2013). National Policy on Information and Communication Technologies (ICT) in Education. https://education.gov.ng.
Fraillon, J., Ainley, J., Schulz, W., Friedman, T., & Duckworth, D. (2019). Preparing for life in a digital world: IEA international computer and information literacy study 2018 international report. Amsterdam: International Association for the Evaluation of Educational Achievement (IEA). https://www.iea.nl/publications/study-reports/preparing-life-digital-world
Fornell, C., & Larcker, D. F. (2016). Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error. Journal of Marketing Research This, 18(1), 39–50.
Gopalan, Y., & Hashim, H. (2021). Enhancing Higher Order Thinking Skills (Hots) Through Literature Components in ESL Classrooms. International Journal of Academic Research in Progressive Education and Development, 10(2), 317–329.
Ghulami, H. R., Rashid, M., Hamid, A. B., & Zakaria, R. (2014). Partial least squares structural equation modeling (PLS-SEM). Journal of Quality Measurement and Analysis, 10(1), 1–16.
Hair, Joseph F., Gabriel, M. L. D. S., & Patel, V. K. (2014). Amos covariance-based structural equation modeling (CB-SEM): Guidelines on its application as a marketing research tool. Revista Brasileira de Marketing, 13(02), 44–55. https://doi.org/10.5585/remark.v13i2.2718
Henseler, J., Ringle, C. M., & Sarstedt, M. (2014). A new criterion for assessing discriminant validity in variance-based structural equation modeling. Journal of the Academy of Marketing Science, 43(1), 115–135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11747-014-0403-8
Indrawati, & Haryoto, K. S. (2015, August). The use of modified theory of acceptance and use of technology 2 to predict prospective users’ intention in adopting TV streaming. Paper presented at Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Computing and Informatics, Istanbul, Turkey.
Jambulingam, M. (2013). Behavioural intention to adopt mobile technology among tertiary students. World Applied Sciences Journal, 22(9), 1262–1271. doi:10.5829/idosi.wasj.2013.22.09.2748
Jaradat, M. I. R. M., & Banikhaled, M. (2013). Undergraduate students’ adoption of website-service quality by Applying the unified theory of acceptance and use of technology (UTAUT) in Jordan. International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, 7(3), 22–29.
Johnson, S. D., Aragon, S. R., Shaik, N., & Palma-Rivas, N. (2000). Comparative analysis of learner satisfaction and learning outcomes in online and face-to-face learning environments. Journal of Interactive Learning Research, 11(1), 29–49.
Ju, B. &Albertson, D. (2015). Examining user-driven factors for intentions to use video digital libraries. Proceedings of the Association for Information Science and Technology, 52(1), 1–4. doi:10.1002/pra2.2015.145052010087
Kabir, F.S. (2018). Correlation of Awareness and Usage of Mobile Devices amongst Facilitators and Students of Distance Education in Nigeria. ATBU Journal of Science, Technology and Education (JOSTE). Vol. 6 (3), September, 2018. Abubakar Tafawa Balewa University, Bauchi.
Lwoga, E.T. and Komba, M. (2015), "Antecedents of continued usage intentions of web-based learning management system in Tanzania", Education + Training, Vol. 57 No. 7, pp. 738-756. https://doi.org/10.1108/ET-02-2014-0014
Maduku, D. K. (2015). An empirical investigation of students’ behavioral intention to use e-books. Management Dynamics: Journal of the Southern African Institute for Management Scientists, 24(3),3–20.
Mtebe, J. S., & Raisamo, R. (2014). Investigating students’ behavioural intention to adopt and use mobile learning in higher education in East Africa. International Journal of Education and Development using Information and Communication Technology (IJEDICT), 10(3), 4–20.
Nikolopoulou, K., & Gialamas, V. (2013). Barriers to the integration of computers in early childhood settings: Teachers’ perceptions. Education and Information Technologies, 20(2), 285-301.
Shittu, A.T., Kareem W. B.& S.C. Tukura (2019). Science lecturers’ perceptions and self-efficacy towards use of computer-mediated technologies. Journal of Research in Science and Vocational Education, 1 (1), 222-233
Sheeja, N. K. (2013). Undergraduate students’ perceptions of digital library: A case study. International Information & Library Review, 42(3), 149–153. doi:10.1080/10572317.2010.10762859
Thomas, A., Peterson, D., & Abebe, F. (2019). Adopting TETCs in integrated elementary mathematics and technology coursework: A collaborative self-study of two teacher educators. Journal of Technology and Teacher Education, 27(4), 499-525.
Tokmak, H. S., Yelken, T. Y., & Konokman, G. Y. (2013). Pre-service Teachers’ Perceptions on Development of Their IMD Competencies through TPACK-based Activities. Journal of Educational Technology & Society, 16(2), 243–256.
Vasconcelos, P., Furtado, E. S., Pinheiro, P., & Furtado, L. (2020). Multidisciplinary criteria for the quality of e-learning services design. Computers in Human Behavior, 107, 105979.
Venkatesh, V., Morris, M. G., Davis, G. B., & Davis, F. D. (2003). User acceptance of information technology: Toward a unified view. MIS Quarterly, 27(3), 425–478. Retrieved from March 2, 2016 http://www.cob.calpoly. edu/∼eli/Class/p25.pdf. doi:10.2307/30036540.
Wijaya, T.T.; Cao, Y.; Weinhandl, R.; Yusron, E.; Lavicza, Z. (2022). Applying the UTAUT Model to Understand Factors Affecting Micro-Lecture Usage by Mathematics Teachers in China. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ math10071008 Academic Editor
Yaki, A. A., Koroka, M. U. S. & Shuaibu, A. E (2021). Determinants of Science Technology, Engineering and Mathematics (STEM) Undergraduate University Students’ Entrepreneurship Behavioural Intention. International Journal of Education and Training (InjET) 7(1), 1 - 8
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17509/jsl.v8i1.75651
Data citation
Graphic Abstract
Refbacks
- There are currently no refbacks.
Copyright (c) 2025 Yaki A. Akawo, Mustapha M. Tajordeen, Kabir S. Fatima, Hussain B. Mufida

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 4.0 International License.


Jl. Dr. Setiabudhi 229 Bandung 40154, West Java, Indonesia











